The present value of an annuity is the current value of future payments from an annuity, given a specified rate of return, or discount rate. The payments are at the end of the payment income tax calculator intervals, and both the compounding frequency and the payment frequency are the same (both quarterly). Because this is a simple annuity, an interest rate conversion is not required.
Using the TI BAII Plus Calculator to Find the Future Value for Annuities Due
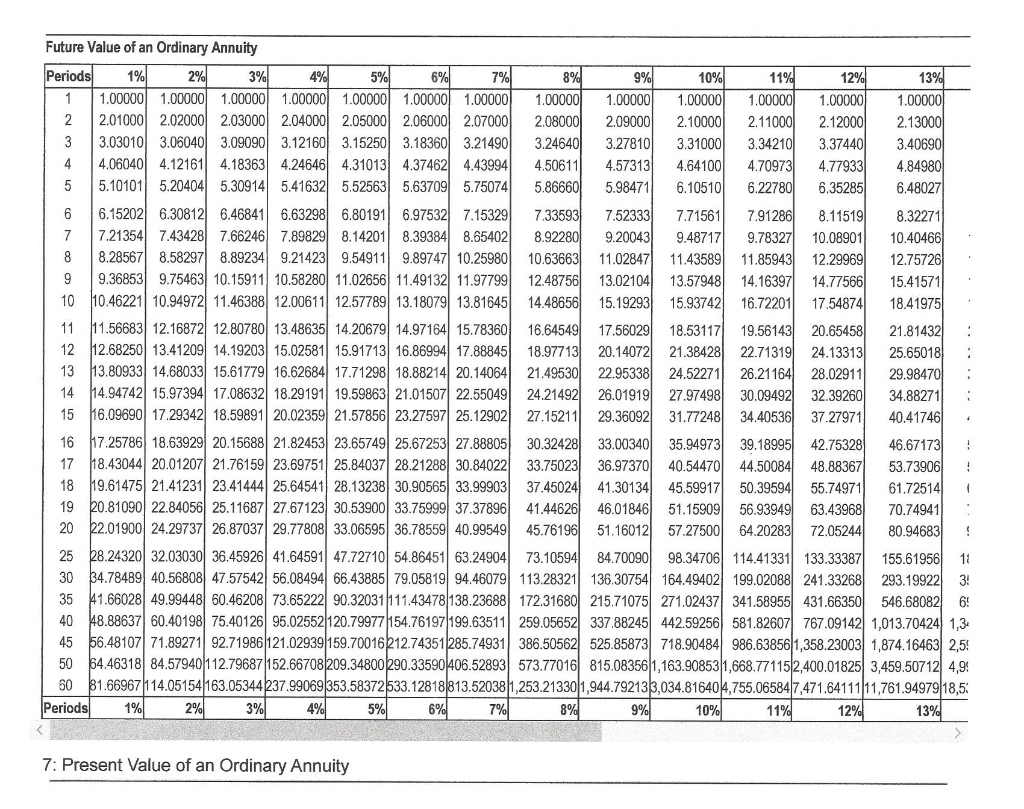
Clearly, solving this would be tedious and time consuming—not to mention prone to error. By plugging in the values and solving the formula, you can determine the amount you’d need to invest today to receive the future stream of payments. In this example, with a 5 percent interest rate, the present value might be around $4,329.48. Let’s say you anticipate receiving payouts at the end of the annuity period—that’s how an ordinary annuity works. If you don’t have access to an electronic financial calculator or software, an easy way to calculate present value amounts is to use present value tables. You can view a present value of an ordinary annuity table by clicking PVOA Table.
How to Calculate the Present Value of an Annuity
However, you can still use our present value of annuity calculator to solve more complex financial issues. In this section, you can familiarize yourself with this calculator’s usage and its mathematical background. If you read on, you can learn what the annuity definition is, what is the present value of annuity as well as how to use this annuity payment calculator. Besides, you can find the annuity formulas and get some insight into their mathematical background.
How to use our annuity calculator?
Therefore, the present value of five $1,000 structured settlement payments is worth roughly $3,790.75 when a 10% discount rate is applied. Let’s assume you want to sell five years’ worth of payments, or $5,000, and the factoring company applies a 10 percent discount rate. Earlier cash flows can be reinvested earlier and for a longer duration, so these cash flows carry the highest value (and vice versa for cash flows received later). An annuity table is a tool used mostly by accounting, insurance or other financial professionals to determine the present value of an annuity.
- The present value of an annuity can be used to determine whether it is more beneficial to receive a lump-sum payment or an annuity spread out over a number of years.
- Annuity tables are visual tools that help make otherwise complex mathematical formulas much easier to calculate.
- As mentioned, an annuity due differs from an ordinary annuity in that the annuity due’s payments are made at the beginning, rather than the end, of each period.
- All you have to do is multiply your annuity payment’s value by the factor the table provides to get an idea of what your annuity is currently worth.
Given this information, the annuity is worth $10,832 less on a time-adjusted basis, and the individual should choose the lump sum payment over the annuity. In such cases, there will be multiple time segments that require you to work from left to right through the timeline in order to find the future value at the end of the annuity. The future value at the end of one time segment becomes the present value in the next time segment.
Present Value of a Growing Annuity (g ≠ i) and Continuous Compounding (m → ∞)
See how different annuity choices can translate into stable, long-term income for your retirement years. We specialize in helping you compare rates and terms for various types of annuities from all major companies. Financial calculators also have the ability to calculate these for you, given the correct inputs. These recurring or ongoing payments are technically referred to as annuities (not to be confused with the financial product called an annuity, though the two are related). If you were to receive $1,000 at the end of the year instead, you would only have that $1,000. In this scenario, the future $1,000 is effectively worth $990 today because you missed out on the opportunity to earn that 1% interest over the year.
An ordinary annuity is a series of recurring payments that are made at the end of a period, such as payments for quarterly stock dividends. An annuity due, by contrast, is a series of recurring payments that are made at the beginning of a period. So, for example, if you plan to invest a certain amount each month or year, FV will tell you how much you will accumulate as of a future date. If you are making regular payments on a loan, the FV is useful in determining the total cost of the loan. FV is a measure of how much a series of regular payments will be worth at some point in the future, given a specified interest rate. With ordinary annuities, payments are made at the end of a specific period.
It’s all simplified for you in this turn-key system that takes just 30 minutes per month. If you’re looking for an investment strategy that goes beyond “buy and hold” while controlling risk and requiring as little as 30 minutes a month to manage, this is the answer. It’s critical to know the present value of an annuity when deciding if you should sell your annuity for a lump sum of cash. Calculating present value is part of determining how much your annuity is worth — and whether you are getting a fair deal when you sell your payments.
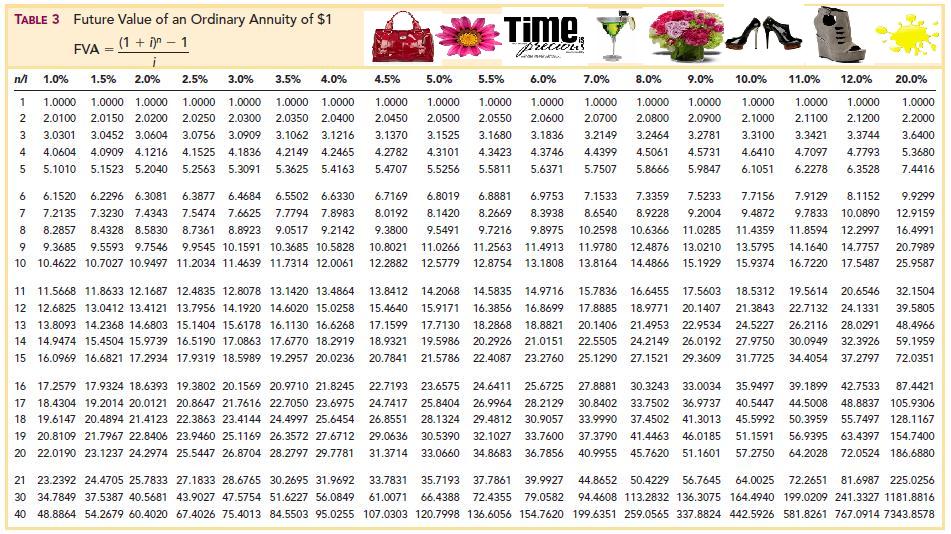
Therefore, the future value of your regular $1,000 investments over five years at a 5 percent interest rate would be about $5,525.63. You can use an online calculator to figure both the present and future value of an annuity, so long as you know the interest rate, payment amount and duration. McGillivray points out that life insurers rely on internal data as well as tables from sources like the Society of Actuaries to do their own proprietary calculations about annuities. Typically, insurers don’t share these calculations, which can include assumptions about a customer’s life expectancy. The goal is to provide you with guaranteed income in the future, typically in retirement. Similarly, the formula for calculating the PV of an annuity due takes into account the fact that payments are made at the beginning rather than the end of each period.
Subscribe to be the first one to receive latest news, exclusive updates and member-only offers and promotions.